www.heavydutydiag.com
The body group is the support of the diesel engine and the installation base for the crankshaft connecting rod mechanism, valve mechanism and other major components of the diesel engine mechanism and system. The diesel engine body group mainly consists of the cylinder block (or engine block, crankcase), cylinder gasket, cylinder head, cylinder liner and oil pan
Deutz Diagnostic Tool Communicator for Deutz Engine DECOM Controllers
(1) Structure of the engine body The engine body of the FL413F/513 diesel engine adopts a gantry structure (as shown in Figure 2-2). This structure has a relatively high engine body rigidity. The upper part of the V-shaped engine body is two cylinder liner mounting planes at a 90° angle to each other. The injection pump bracket and fan transmission box are installed in the middle, and the lower part is the oil pan joint surface.
The cylinder liner mounting plane is at a 45° angle to the oil pan joint surface. The engine body is cast from gray alloy cast iron. The hardness is 180~250HB. The center-to-center distance between the cylinder liner mounting holes on the cylinder liner mounting plane is 165mm, and the hole diameter is 139mm.
Due to the parallel connecting rod mechanism, the left and right cylinder liner mounting holes are not aligned, but offset by 29mm. ① The crankcase main bearing bottom hole has a diameter of φ101 (+0.022)mm. The third cross-plate is used exclusively for thrust positioning.
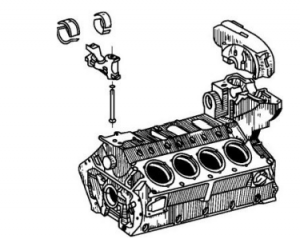
Figure 2-2 F8L413F diesel engine block The main bearing cap is secured simultaneously with two M16×1.5mm vertical bolts and two M10mm horizontal bolts. The main bearing cap is made of QT50-5 ductile iron. ② A φ22.5mm main oil gallery bottom hole is cast in the crankcase, and a φ22mm oil pipe is installed; the main oil gallery communicates with the main bearing bottom hole.
(2) Engine body features The FL413F/513 diesel engine body has the following features. ① High degree of universality, serialization, and standardization. Models with different cylinder numbers have basically the same structural elements except for the length. ② Compact structure and small external dimensions. The horizontal width of the oil pan joint surface is only 265mm, which is convenient for installation on the equipment. ③ The transmission gearbox and crankcase are cast as one piece, which increases the overall rigidity of the rear part of the crankcase and the crankcase. ④ In addition to two vertical bolts, the main bearing cover and the engine body are fastened with two horizontal bolts. This better ensures the rigidity of the engine body and is also conducive to reducing the noise of the diesel engine. (3) Main damage modes of the cylinder block The main damage modes of the diesel engine block are: ① Due to the breaking of the connecting rod bolt; ② Due to the burning of the bearing, the bottom hole of the main bearing is deformed, out of round or the coaxiality is deteriorated; ③ Due to overload operation or other factors, the cross-partition of the bottom hole of the main bearing is deformed or cracked; ④ Abnormal damage caused by other reasons
2024 Deutz SerDia 4.0 SerDia2010 14.1.9.3 Highest Level 6 Diagnostic Software

.
(4) Inspection points of the engine block (crankcase or cylinder block) The engine block of the diesel engine is the basic component of the diesel engine, and all moving parts are installed on it. Therefore, the quality of the engine block directly affects the running stability and reliability of the entire diesel engine. When overhauling the diesel engine, the quality of the engine block should be carefully checked, focusing on the following parts. ① The quality of the bottom hole of the main bearing of the engine block, that is, check whether the main shaft hole is out of round, whether there are cracks or bearing rotation, and whether the coaxiality of all holes is out of tolerance. ② Whether there are cracks or looseness in the engine block water jacket, cross-partition, etc. ③ Check whether the mounting surfaces (mainly the mounting surfaces with the cylinder liner and cylinder head) are deformed or have pits, corrosion spots, etc. ④ Check whether the relevant oil channels (such as the main oil channel or the diesel oil channel of the single pump diesel engine) are intact. The engine body can only be used after it is checked to confirm that there are no quality problems. Otherwise, it should be repaired before use.
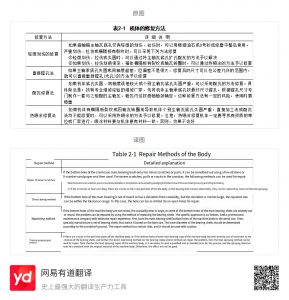
(5) Repair method of engine body cross partition crack When the diesel engine is short of oil and causes failures such as bearing burning and shaft seizure, it may cause the bottom hole of the main bearing of the engine body to wear and become out of round, deformed or cracked. At this time, the bottom hole of the main bearing of the engine body needs to be repaired. The repair points are shown in Table 2-1.
If the technology is good enough, the best repair method should be to use the thermal spray method to repair the engine body (cylinder block) because it can completely restore the original standard size and precision requirements of the bottom hole of the main bearing of the engine body. A successful case in this regard is the use of thermal spraying to repair the engine body of several F12L513 diesel engines. After years of use, no quality problems have occurred in the repaired parts.
Deutz Serpic 2012 EPC Download & Installation Service Finial Version
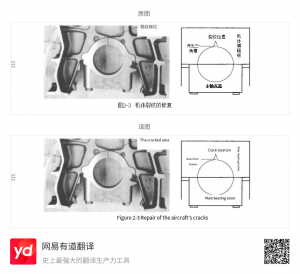
As shown in Figure 2-3, if a crack appears in the cross-plate of a diesel engine (cylinder block) at the location shown (left image in Figure 2-3), it can be repaired using the following methods: ① Use a grinding wheel or other cutting device to create a triangular groove at the crack (the size can be adjusted according to the actual crack condition).
② Heat the cross-plate to a certain temperature (the specific temperature depends on the engine block material) and maintain it at this temperature for a certain period of time.
③ Use the same hardfacing (or thermal spray) material as the engine block for hardfacing or spraying, ensuring that the entire main bearing bottom hole is welded or sprayed.
④ After the engine block has completely cooled to room temperature, perform precise boring on a jig boring machine, ensuring that the dimensions and coaxiality of all bottom holes meet the engine’s technical requirements.
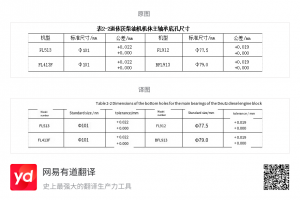
Regardless of the method used to repair a damaged engine block, the key is to know the standard dimensions and tolerances of the cylinder block main bearing bottom holes. These can be determined through pre-measurement and analogy. The standard dimensions of the bottom hole of the main bearing of some Deutz air-cooled diesel engines are shown in Table 2-2.
Special note: When using the thermal spray method to repair the bottom hole of the main bearing of the diesel engine cylinder block, before precision machining the hole diameter, the main bearing cover bolts must be tightened according to the main shaft bearing cover bolt tightening torque requirements. If the bolts are not tightened properly, the precision machined bottom hole will be deformed, causing the crankshaft to rotate with difficulty or even unable to rotate. This requires special attention.
(6) Cleaning requirements for the bottom hole of the cylinder head bolt After the FL413F/513 diesel engine is disassembled for overhaul or on-site troubleshooting, a large amount of dust or debris will fall into the bolt bottom hole (as shown in Figure 2-4). If it is not cleaned up, it will seriously affect the tightening of the cylinder head bolts. Therefore, when performing on-site maintenance work such as disassembling the cylinder head, special attention should be paid to the cleaning of the cylinder head bolt bottom hole. ① Before removing the cylinder head bolts, clean as much dust and debris as possible from the area around the bolts to prevent them from falling into the bolt base holes. If dust or debris falls into the bolt base holes, it may cause the cylinder head to not be tightened to the required degree (the required tightening torque has been met, but the cylinder head is not actually tightened). ② If debris or dust accidentally falls into the bolt base holes while removing the cylinder head bolts, be sure to remove all of it. Never install and tighten the bolts without cleaning the bolt base holes. ③ The basic method for removing dust and debris from the bolt base holes is as follows:
a. Pour a certain amount of kerosene (or diesel) into the bolt base holes, let them soak for a certain period of time, then use high-pressure air to blow out the dust and debris.
air to blow out the dust and debris. b. If high-pressure air cannot blow the bolt holes clean, use the following method to completely remove accumulated dust and debris: Take a used cylinder head bolt, grind the bottom flat, and grind three vertical grooves approximately 5mm deep in the threaded area.
Manually screw the bolt in and out repeatedly until it is completely free of dust and debris.
Note: The above step (cleaning dust from the bolt holes) is extremely important. Failure to do so may result in insufficient tightening of the cylinder head bolts, causing the diesel engine to malfunction. Similar failures have occurred numerous times, and this is especially important when troubleshooting problems such as “cylinder scuffing” on-site.



